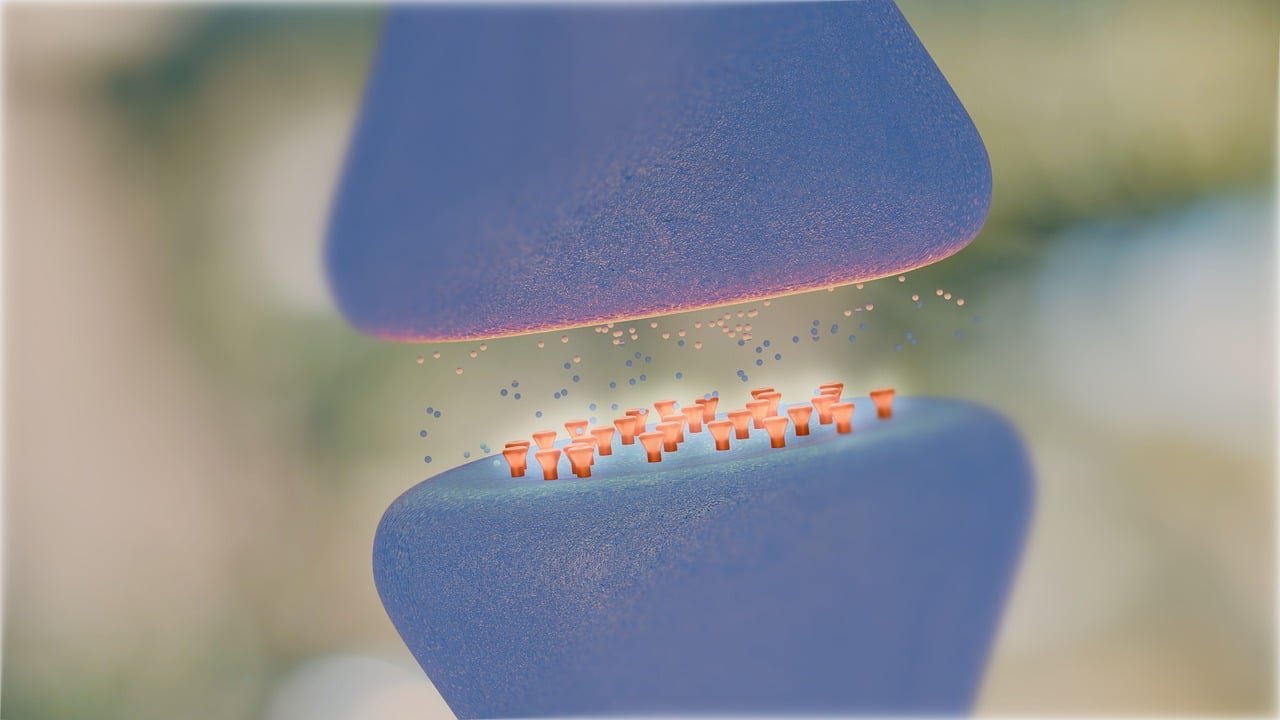
Emotional healing is a multifaceted process shaped by various elements, including the intricate workings of our brain chemistry. Neurotransmitters, the brain’s chemical messengers, play an essential role in regulating mood, emotions, and overall mental well-being. Gaining a deeper understanding of how these neurotransmitters operate can illuminate the path to emotional recovery and healing from mental health issues.
Understanding Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that enable communication between neurons in the brain. They influence a vast array of physiological functions, including mood regulation, sleep patterns, appetite, and memory. Notable neurotransmitters include serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Each of these chemicals has a specific function that significantly impacts our emotional state and stress responses. For those seeking assistance with emotional healing, a ketamine therapy clinic San Diego can provide innovative treatment options that target neurotransmitter imbalances.
Serotonin’s Influence on Mood
Often dubbed the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, serotonin is closely linked to feelings of happiness and emotional well-being. Low levels of serotonin have been linked to several mental health conditions, including depression and anxiety disorders. Engaging in activities that promote serotonin production—such as physical exercise, spending time in nature, or practicing mindfulness—can enhance emotional resilience. Therapies and medications that increase serotonin availability can also assist individuals in their journeys toward emotional recovery.
Dopamine and the Reward System
Dopamine is an essential neurotransmitter that plays a vital role in the brain’s reward systems. It is responsible for regulating feelings of pleasure, motivation, and reward. When we achieve something or enjoy a positive experience, dopamine levels increase, reinforcing those behaviors. This connection underscores the importance of participating in rewarding activities during the emotional healing process. Setting and accomplishing small goals can stimulate dopamine production, fostering a sense of achievement and motivation.
Norepinephrine and Stress Regulation
Norepinephrine helps prepare us for fight-or-flight situations, but when its levels are imbalanced, it can lead to anxiety and mood disorders. Incorporating stress management techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or mindfulness meditation, can be effective in regulating norepinephrine levels. These practices may promote emotional healing by reducing stress and anxiety, creating a more balanced emotional state.
GABA’s Calming Properties
GABA is essential for reducing anxiety and promoting relaxation. Many people struggling with emotional challenges find relief through activities that enhance GABA levels, such as yoga, meditation, or specific dietary choices. Additionally, some medications that increase GABA activity have proven effective in treating anxiety disorders, highlighting the importance of this neurotransmitter in emotional recovery.
The Interconnected Nature of Neurotransmitters
It’s vital to understand that neurotransmitters do not function independently; they interact in complex networks that influence our emotional states. For instance, serotonin can affect dopamine levels, while stress can impact GABA activity. This interplay indicates that addressing one neurotransmitter may have broader implications for others, reinforcing the necessity for a holistic approach to emotional healing.
Conclusion
Neurotransmitters are integral to the process of emotional healing, influencing our mood, stress responses, and overall mental health. By comprehending their functions, individuals can take proactive steps toward recovery through lifestyle adjustments, therapeutic interventions, or medication. By nurturing healthy neurotransmitter activity, we can enhance our emotional well-being and navigate the journey of healing with greater resilience and optimism.